Crocin
Description
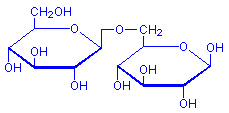
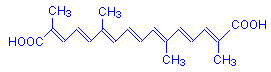
The active colouring constituent of saffron is crocin, which is a di-gentabiose ester of crocetin, although the exact structure is not given. The dye is obtained from the stigmata of Crocus sativus, which are collected by hand, so the dye is expensive. Although used in the past for many purposes, today saffron is used primarily as a food colour and spice.
Its histological use is largely confined to the HPS staining technique, in which it colours connective tissue yellow in contrast to the pink cytoplasm of phloxine B. Due to the expense of the saffron the method is not common, and modifications employing tartrazine as in the phloxine-tartrazine method or chrome fast yellow 8GL as in a modified yellowsolve have been suggested as substitutes.
References
- R. D. Lillie.
Conn’s Biological Stains
Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD., U.S.A. - Susan Budavari, Editor,
The Merck Index, Ed. 12
Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA - Colour Index
Society of dyers and colourists, UK.