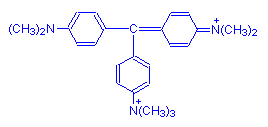
Light green
Description
Methyl green has seven methyl groups rather than crystal violet's six. This seventh group is easily lost and the dye reverts to crystal violet. For that reason, there is invariably a quantity of crystal violet mixed with methyl green. If it is important to ensure there is no crystal violet present, the solution of methyl green may be washed with chloroform to extract the crystal violet. This is commonly done when using it to demonstrate nucleic acids by the Unna-Pappenheim stain, in conjunction with Pyronin Y.
Methyl green has also been recommended as suitable for the metachromatic demonstration of amyloid, and it is probable the contaminating crystal violet is then necessary.
The Merck Index and Aldrich use the name methyl green for a closely related dye, ethyl green, in which the seventh group is an ethyl group rather than methyl. The two dyes are very similar, and are probably interchangeable. It has been suggested that ethyl green is often the dye actually provided when methyl green is purchased.
Do not confuse this dye with the acid dye usually meant when light green is specified and which is used in Masson's trichrome.
Compare to ethyl, iodine, and malachite greens.
References
- R. D. Lillie.
Conn’s Biological Stains
Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD., U.S.A. - Susan Budavari, Editor,
The Merck Index, Ed. 12
Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA - Edward Gurr, 1971
Synthetic dyes in biology, medicine and chemistry
Academic Press, London, England.