Walter's Trichrome
for Elastic and Collagen
Materials
Solution A
| Material | Amount | |
|---|---|---|
| Ferric ammonium sulphate | 2.5 | g |
| Distilled water | 100 | mL |
Solution B
| Material | Amount | |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphotungstic acid | 2 | g |
| Distilled water | 100 | mL |
Solution C
| Material | Amount | |
|---|---|---|
| Eosin B | 0.7 | g |
| Acid fuchsin, sat. aqu | 4 | mL |
| Unna’s elastic stain | 35 | mL |
| Ethanol, 50% | 35 | mL |
| Glycerol | 40 | mL |
Tissue Sample
5µ paraffin sections of neutral buffered formalin fixed tissue are suitable. Other fixatives are likely to be satisfactory. Most trichrome stains benefit from picric acid or mercuric chloride fixation. Formalin fixed tissues may benefit from secondary fixation of sections in Bouin’s fluid.
Protocol
- Bring sections to water via xylene and ethanol.
- Place into solution A for 24 hours.
- Rinse quickly with distilled water.
- Place into solution B for 10 minutes.
- Rinse quickly with distilled water.
- Place into solution C for 15-20 minutes.
- Rinse quickly with 95% ethanol until clouds of dye stop being extracted.
- Dehydrate with 100% ethanol for 1 minute.
- Clear with xylene and mount with a resinous medium.
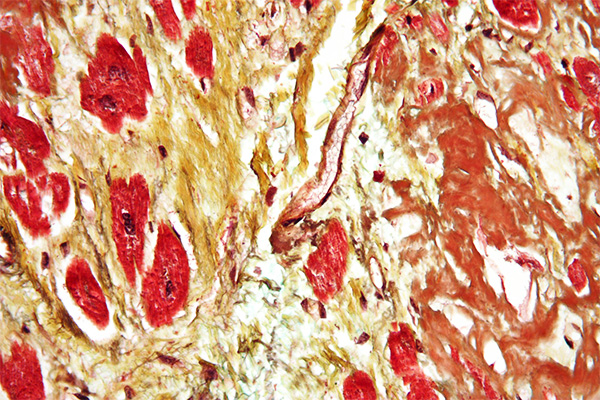
Expected Results
- Nuclei – purple
- Elastic fibres – purple
- Erythrocytes – orange
- Collagen – blue
Notes
- This is a modification of Pasini’s method.
Safety Note
Prior to handling any chemical, consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for proper handling and safety precautions.
References
- Gray, Peter. (1954)
The Microtomist’s Formulary and Guide.
Originally published by: The Blakiston Co.
Republished by: Robert E. Krieger Publishing Co.
Citing:
Walter, (1930)
Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Mikroskopie und für mikroskipische Technik,
v. 46, pp. 458